Parts of Hair Structure – Everything You Need to Know
Parts of Hair Structure –
Hair is an essential part of our identity and is made up of many different parts. Understanding the structure of hair can help us care for it better and make sure it remains healthy.
In this article, we’ll discuss the different parts of hair, the number of parts it has, and their functions. We’ll also be looking at the five main structures of hair and how they all contribute to healthy hair.

- What are the 3 different parts of hair structure?
- How does hair grow? The hair growth cycles
- What is Trichology and why is it important?
- Are there 3 parts of hair or more and what are their functions?
- What are the 5 main structures of hair?
- What are the 4 parts of hair anatomy?
- What you need to know about hair anatomy
- Anatomy and parts of hair structure
- The Papilla
- What are the functions of human hair?
- How many different kinds of hair are on the human body?
What are the 3 Parts of Hair Structure?
Hair is composed of three main parts –
☝️The hair follicle – where the hair grows out of the scalp.
✌️The hair shaft – the length that we can see and gets damaged. Also called the “cuticle”.
👌 The cortex – the internal structure of what makes up a hair strand. These have
What Are the Different Parts of Hair Structure?
The scalp is part of the skin which is actually the largest organ of the body. It’s made up of several components, including the epidermis, dermis, sebaceous glands, and arrector pili muscles.
The hair shaft refers to the visible part of the hair, which is made up of proteins called keratin.
How Does Hair Grow?
Hair growth is a complex process that involves many different parts of the body.
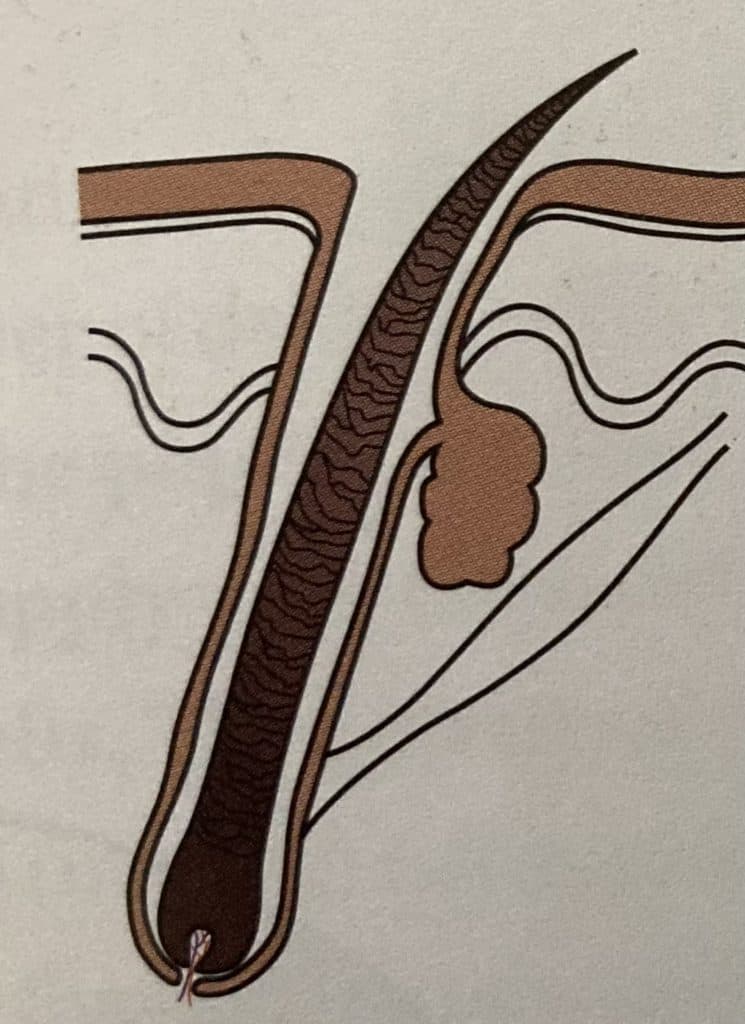
Hair growth starts at the root of the hair follicle, which is located in the dermal layer of the skin.
The cells at the base of the follicle divide and grow to form the hair shaft, which is made up of a protein called keratin. As the cells at the base of the follicle divide, new cells are pushed up through the follicle and out of the scalp.
On average, hair grows about 0.5 – 1 inch per month or 6 – 12 inches per year.

Hair Growth Cycles – Anagen, Catagen, Telogen Phases
Phase 1 – Anagen
Hair growth is a cyclical process. It begins with the anagen phase, which is the period of active hair growth.
During this phase, cells in the hair follicle divide rapidly, causing the hair to grow approximately half an inch per month. This phase can last anywhere from two to seven years.
Phase 2 – Catagen
Next is the catagen phase, which is a transitional phase lasting approximately two weeks. During this phase, hair growth slows and the hair follicle begins to shrink.
Phase 3 – Telogen
The third phase is the telogen phase, which is the resting phase. During this phase, the hair follicle remains inactive and the existing hair falls out. This phase lasts approximately three months.
Finally, the cycle begins again with the anagen phase, beginning the cycle again, when the hair follicle reactivates and a new hair begins to grow. This process repeats itself throughout the lifetime of the hair.
What is trichology and why is it important in parts of hair structure?
Trichology is the scientific study of the hair and scalp. It is a branch of dermatology, or the study of skin, and involves the diagnosis and treatment of hair and scalp disorders.
Trichology is important because it helps to identify and treat a variety of issues related to the hair and scalp, ranging from common diseases such as alopecia to less common conditions such as trichotillomania.
It is also important to be aware of the role nutrition and lifestyle plays in hair health, which trichologists can help to identify and address.
Hairstylists, cosmetologists, and barbers don’t need to be trichologists but are welcome to study and become an expert! They are however, trained and familiar with all that is listed in this article.
Are There 3 Parts of Hair Structure or More? What Are Their Functions?
Hair is composed of three main parts –
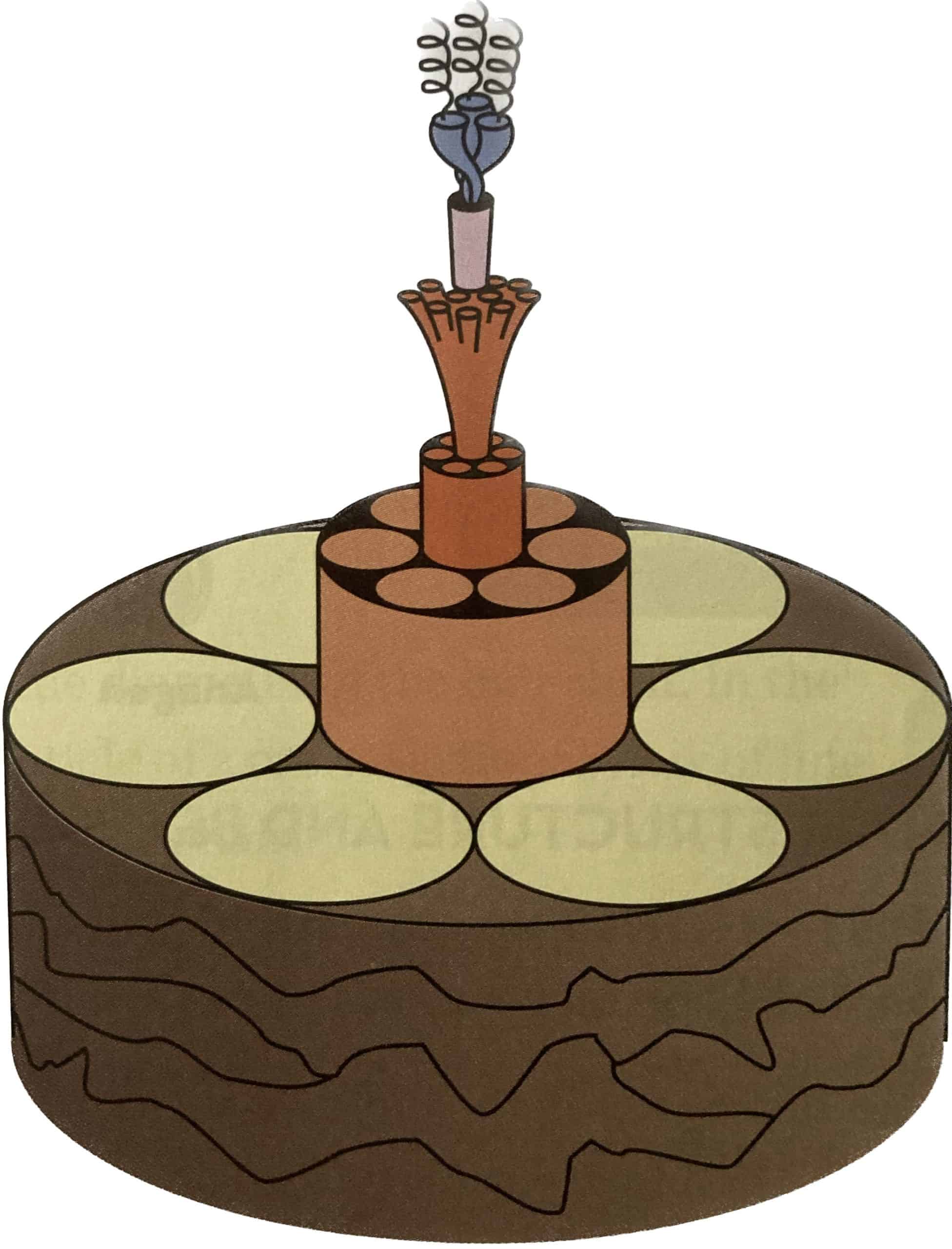
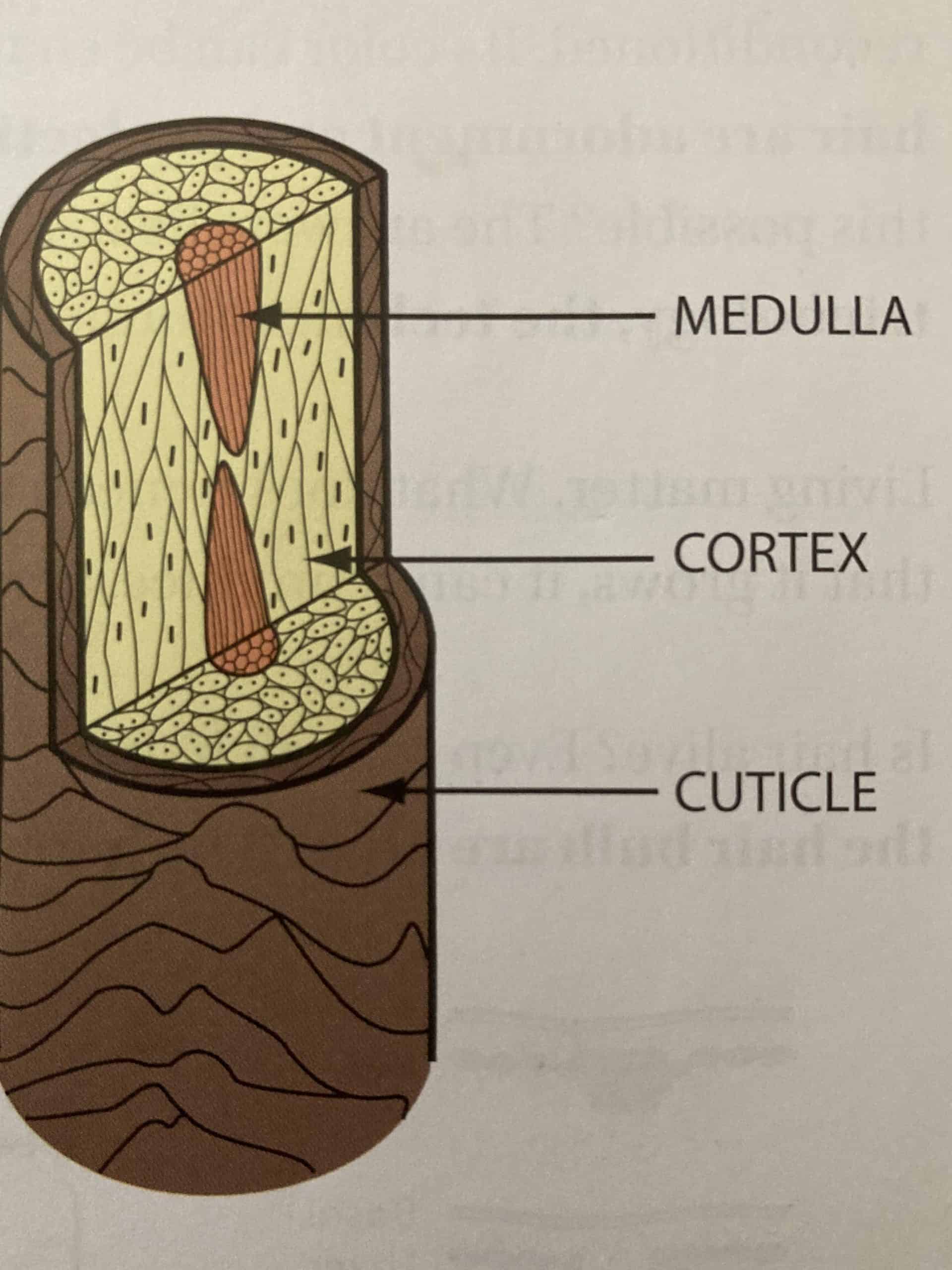
The cuticle, cortex, and medulla.
The cuticle is the outermost layer of the hair, and it’s made up of overlapping layers of keratinized cells. It helps protect the inner layers of the hair and can be damaged by over-styling or chemical treatments.
The cortex is the middle layer of the hair and contains the pigment that gives hair its color.
The medulla is the innermost layer of the hair, and it’s mostly composed of air pockets.
All three of these parts of hair work together to create the structure and texture of our hair.
The cuticle helps protect the inner layers from damage, the cortex gives our hair its color, and the medulla helps create the texture of our hair.
What Are the 5 Main Structures of Hair?
The five main structures of hair are the cuticle, cortex, medulla, the sebaceous glands, the arrector pili.
The Cuticle
The cuticle is the outermost layer of the hair, and it helps protect the inner layers of the hair.
The Cortex
The cortex is the middle layer of the hair, and it contains the pigment that gives hair its color. It also helps protect the inner layers from damage and gives hair its color.
The Medulla
The medulla is the innermost layer of the hair, and it’s mostly composed of air pockets, as well as helps create the texture of our hair.
The Sebaceous Glands
The sebaceous glands are located in the hair follicle, and they secrete sebum, which is an oily substance that helps keep the hair and scalp moisturized.
However the sebaceous glands aren’t a part of the hair strand itself, but of the scalp, they play a very important roll in hair health. If the scalp isn’t hydrated and becomes too dry it affects how the hair grows.
The Arrector Pili Muscles
Lastly, the arrector pili muscles are located in the hair follicle, and they help give hair its shape.
Though the arrector pili aren’t a part of the hair itself, it plays an important role in hair health and development.
All five of these structures work together to help create healthy, strong hair.
What are the 4 Parts of Hair Anatomy?
Hair anatomy and understanding the parts of hair structure is important for trichologists and hairstylists.
Knowing the parts and functions of hair can help you, as a professional, or as a non-pro provide the best care to your clients or your own hair.
Let’s take a look at the four parts of hair anatomy and what you need to know about hair structure and anatomy.
What You Need to Know about Hair Anatomy
Hair anatomy is in short, the summary of what we discussed above.
The three parts of hair anatomy are the cuticle, cortex, medulla.
👉 The cuticle is the outermost layer of the hair. It is made of overlapping cells and is responsible for the protection and smoothness of the hair. The cuticle is the outer layer of the hair and is responsible for the shine and texture of the hair.
👉 The cortex is the main body of the hair, which is composed of proteins and pigments.
👉 The medulla is the innermost layer of the hair and is made of air-filled cells. It is responsible for the strength of the hair.
Parts of Hair Structure Inside the Medulla
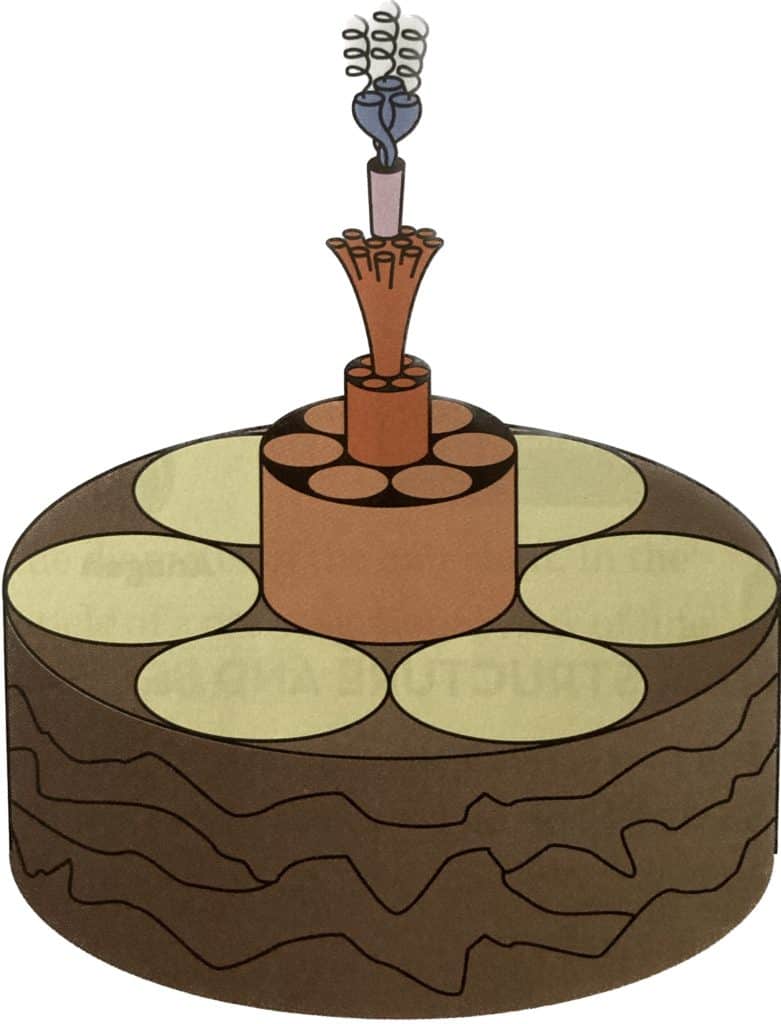
When we move further into the medulla we then find chemical bonds.
These bonds are responsible for the strength, elasticity, and flexibility of the hair as well as its shape and ability to hold its shape.
The medulla is a layer of tissue that can be found inside the hair shaft and is located between the cortex and the cuticle.
It is filled with air spaces and is highly porous.
It is made up of protein, which forms chemical bonds that give the hair its unique properties.
The chemical bonds within the medulla can be divided into two main categories: covalent and disulfide bonds.
Covalent bonds are strong and are formed between two atoms when they share electrons.
This type of bond forms the backbone of the protein structure that makes up the medulla. It is important because it is what gives the hair its strength, elasticity, and flexibility.
Disulfide bonds are also found in the medulla, and they are much weaker than covalent bonds. This type of bond is essential for providing the hair with a certain level of strength and shape.
Disulfide bonds are formed when sulfur atoms link two protein molecules together. This type of bond is responsible for the shape of the hair and its ability to remain in place.
The Papilla
The papilla is a critical part of the hair structure and plays an important role in the proper growth and nourishment of hair strands. It contains the dermal papilla cells that produce growth factors and nutrients to promote the formation of new hairs and to nourish the hair follicle.
The papilla also provides the necessary anchoring to keep the hair follicle in its place in the scalp.
Where is the papilla?
The papilla is a small, conical-shaped structure located at the base of each hair follicle in the skin of the scalp.
It is composed of connective tissue and is responsible for the formation of hair strands.
What role does the papilla play in hair structure?
The papilla is a crucial part of the hair structure as it plays several important roles. It contains the dermal papilla cells, which are responsible for the formation of new hair strands.
These cells also help in the nourishment of the hair follicle and its growth.
The papilla is also responsible for the anchoring of the hair follicle in the scalp and the formation of the hair shaft.

What are the functions of the papilla?
The main functions of the papilla are to nourish the hair follicle and to stimulate the growth of new hair strands. The dermal papilla cells produce growth factors that promote the formation of new hairs.
They also contain nutrients that feed the hair follicle and promote its growth. The papilla also provides the necessary anchoring to hold the hair follicle in place in the scalp.
Anatomy and Parts of Hair Structure
In addition to the anatomy of hair, you should also be aware of the structure of hair.
Hair structure is composed of the cuticle, cortex and medulla. All of which we discussed above.
What are the Functions of Human Hair?
Understanding the parts and functions of human hair is essential for trichologists and hairstylists.
Human hair has four main functions –
- Insulation
- Protection
- Regulation of temperature
- Communication
Insulation
Hair helps to insulate our bodies and protect us from the elements. It helps to keep us warm in cold weather and cool when it is hot.
Protection
Hair also provides protection from physical and chemical hazards, as well as from UV radiation.
Regulation of Temperature
Hair helps to regulate the temperature of the skin by absorbing sweat and keeping the body cool.
Communication
Hair also plays a role in communication. It can convey information about a person’s health, age, and social status.
How Many Types of Hair are on the Human Body?

There are six different types of hair on the human body –
- Vellus hair
- Terminal hair
- Lanugo hair
- Androgenic hair
- Sebaceous hair
- Cilia hair
Vellus hair is the soft, fine, short hair that covers the body of infants and most of the body of adults.
It is usually colorless and can vary in thickness.
Terminal hair is the thick, coarse, long hair found on the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes.
It is usually pigmented and is responsible for the appearance of the hair we notice on the body.
Lanugo hair is the fine, downy hair found on the body of newborns. It usually disappears over time.
Androgenic hair is the terminal hair that is stimulated by hormones and is responsible for male-pattern baldness.
Sebaceous hair is the short, fine, colorless hair that is found in the sweat glands and is responsible for the release of sweat.
Cilia hair is the short, fine, colorless hair that is found in the nose and ears and is responsible for trapping dirt and other particles.
Knowing the anatomy and structure of hair can help you, as a professional, provide the best care to your clients.
Additionally, it is important to be aware of the six types of hair on the human body. From vellus to cilia, each type of hair has its own unique role in the body.
Conclusion for Parts of Hair Structure
Hair is an essential part of our identity, and understanding its structure can help us care for it better. Especially as hair professionals caring for our clients.
Hair is composed of three main parts – the cuticle, cortex, and medulla. Additionally, there are five main structures of hair: the cuticle, cortex, medulla, sebaceous glands, and arrector pili muscles.
All of these parts and structures work together to create healthy, strong hair.
By understanding the parts of hair and their functions, we can better care for our hair and keep it looking and feeling its best.
Related Articles to Parts of Hair Structure – Everything you Need to Know
15 Tips to Overcome Bad Haircut Anxiety
How to Wash Hair to Prevent Hair Loss
45 Hairstyles for Thinning Hair – Causes and Solutions
Is My Hair Healthy? – Quiz to do at Home
Keratin Treatment Ruined My Hair! 10 + Tips from a Pro
12 Signs your Hair IS Growing – Tips from a Pro
How to Get Green Out of Hair From Chlorine
📷 All Follicle Photos Taken from Pivot Point Cosmetology Fundimentals Handbook